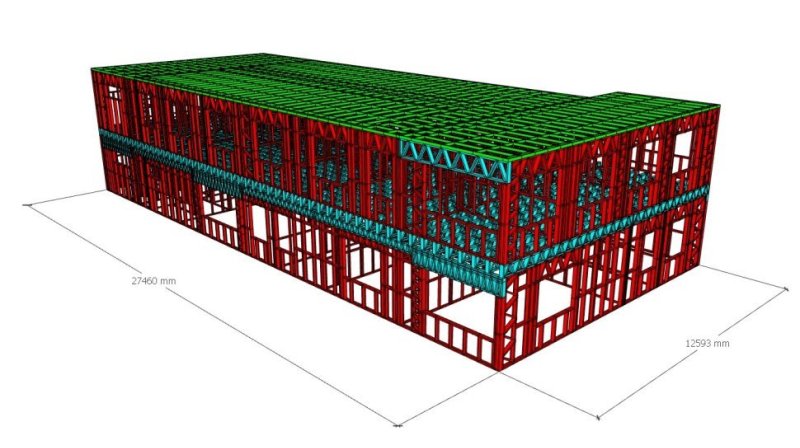
What is a Lightweight Steel-Frame House?
The manufacturing of lightweight steel-frame house structures is a rapidly growing sector in the construction industry, offering fast, cost-effective, and sustainable solutions. These buildings' structural systems are typically made of steel or wood, but steel-frame technology stands out due to its durability and versatility.
What is a Lightweight Steel-Frame House?
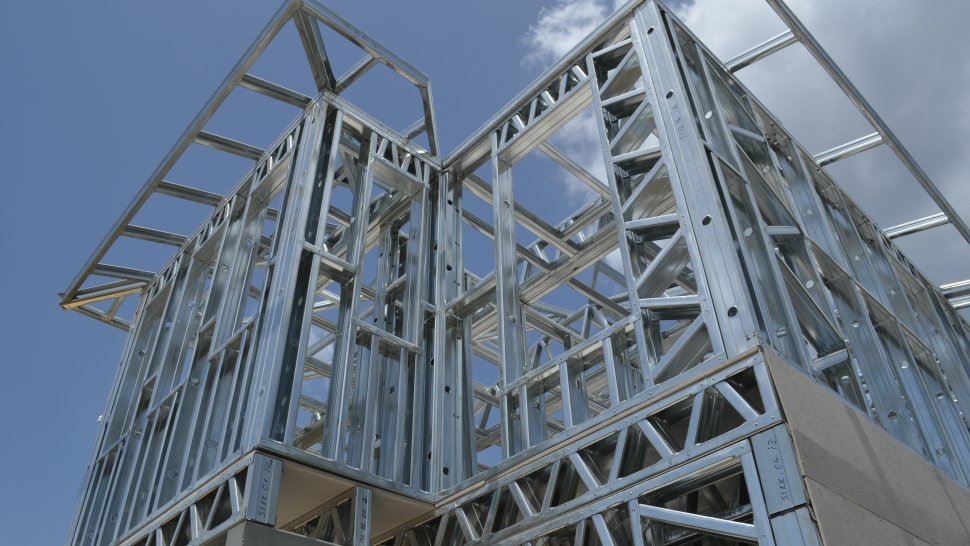
Lightweight steel-frame houses are buildings constructed from prefabricated, modular elements. These elements are manufactured in a factory and can be quickly assembled on-site. The structure is typically composed of galvanized steel profiles or wooden elements, combined with various cladding and insulation materials.
Advantages of Steel-Frame Lightweight Houses
1.) Fast Construction
- The manufacturing and assembly of steel-frame elements are significantly faster than traditional construction methods.
- Since the elements are prefabricated, on-site work is minimized.
2.) Lightweight and Durable Structure
- Steel is a lightweight yet extremely strong material, ensuring the stability and longevity of the building.
- It is resistant to environmental factors such as insects, fungi, and moisture.
3.) Excellent Earthquake Resistance
- The flexibility of steel structures allows them to withstand seismic movements better, making them ideal for earthquake-prone areas.
4.) Cost-Effectiveness
- Using prefabricated elements reduces construction time and labor costs.
- Steel-frame structures require low maintenance, leading to long-term savings.
5.) Sustainability
- Steel is recyclable, making lightweight steel-frame houses an environmentally friendly solution.
- Minimizing construction waste and creating energy-efficient structures contribute to sustainability.
Manufacturing Process
1.) Design and Engineering Preparation
- Creating architectural plans and conducting structural calculations.
2.) Prefabrication
- Manufacturing structural elements such as steel profiles and panels in a factory.
- Integrating insulation and coatings during production.
3.) Transportation
- Delivering the prefabricated elements to the construction site.
4.) On-Site Assembly
- Assembling elements on-site, including walls, roof structures, and other components.
5.) Finishing Work
- After structural completion, installing mechanical, electrical systems, and interior finishes.